When diagnosed with a chronic disease, such as diabetes, they usually experience shock and great confusion. However, this episode must pass so that the corresponding measures can be taken to control the disease and have a good quality of life.
The great secret of patients who have managed to lead a normal life with diabetes has been to adapt their lifestyle habits to be as healthy as possible, changes that at first may not be so easy to achieve but, over time it becomes a habit and not a sacrifice.
Within these habits are aspects such as diet, physical activity, frequent medical control, and other factors that are crucial to maintaining balanced blood glucose and thus preventing the many ailments related to this disease, even reducing the risk of premature death.
Ten recommendations to keep diabetes under control
Living a normal life when suffering from diabetes is a goal that can be achieved if people learn to follow these recommendations, allowing them to keep their body and mind healthy.
Educate yourself about diabetes
The first thing that everyone should do when diagnosed with a disease, whether it is diabetes or any other condition, is to learn about the disease.
Knowing what diabetes is, what its treatments are, what care it requires, and learning about the successful experiences of other people is fundamental for both the diagnosed person and his or her family members since the latter must also adapt to the new reality if they want the patient to remain healthy.
This learning includes knowing how and why to follow the other nine recommendations.
Change the diet
A healthy and balanced diet is undoubtedly the basis for success in the treatment of diabetes; remember that each of the foods consumed has a direct impact on blood glucose levels. Therefore, you must integrate foods that do not affect these levels and eliminate those that do.
To begin with, it is important to be clear that the diet of a person who has diabetes does not have to be very different from that of a healthy person since both should follow a diet in which 3 to 5 meals a day are eaten, always following the recommendations of specialists, both doctors and nutritionists.
However, when suffering from diabetes, the most important thing to take care of in the diet is not to eat large amounts of carbohydrates, especially those of fast absorption, since these are the main culprits of the increase of glucose in the blood, although these are general parameters, since the diet must be personalized.
Exercise regularly
Physical activity is another essential basis for treating diabetes since it is a factor in glucose control and the prevention of many complications associated with elevated glucose levels.
Among the benefits offered by exercise, in addition to controlling glucose, is the reduction of the risk of hypertension and improves blood circulation, in addition to helping to improve mood, which is often affected when suffering from diabetes.
It is only a matter of adapting the physical activity to the conditions of each person, either by age or level of affectation of the disease, so it is recommended to consult with your doctor and a professional trainer to follow their suggestions.
Staying hydrated
When suffering from diabetes, there is a greater probability of dehydration since the high levels of glucose in the blood make the kidneys work harder to eliminate it through urine, which also causes a loss of fluid that can cause the body to dehydrate and symptoms such as thirst.
Although consuming natural juices or water-rich fruits can be a healthy alternative to staying hydrated, as long as sugar is not added, the most beneficial option is to drink plenty of water to avoid increased blood glucose.
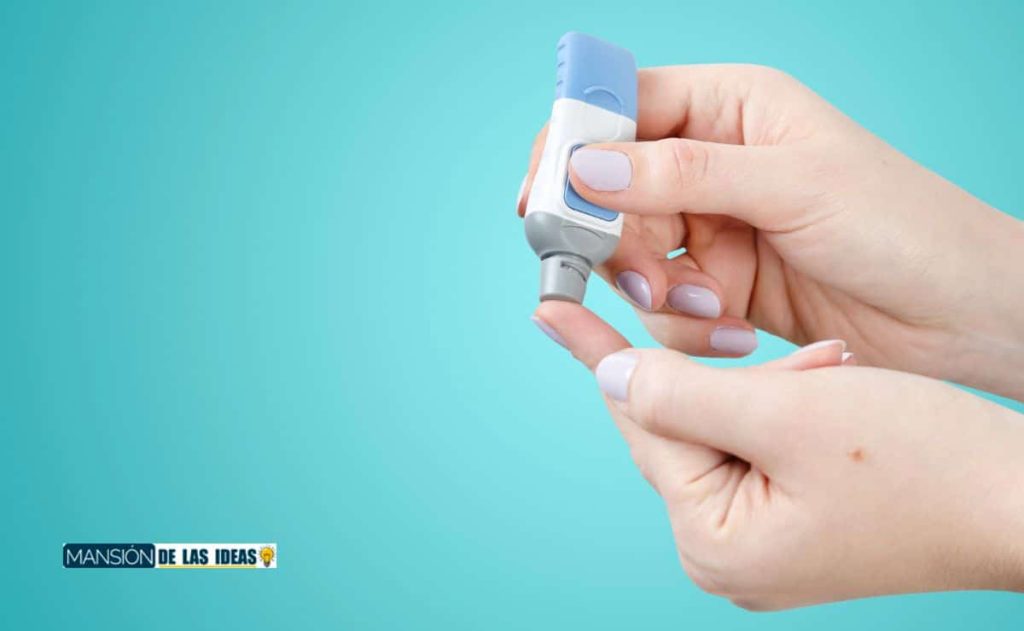
Keep frequent and organized glucose control.
Despite having healthy habits, many factors can lead to uncontrolled glucose levels. Therefore, it is essential that people with diabetes adequately monitor these levels.
Ideally, it is the patient himself or a family member who performs an analysis with the help of a glucometer to know his blood glucose level, whether there is a rise in glucose or what is known as hyperglycemia or a drop, also called hypoglycemia.
The most advisable is to perform between 5 and 6 tests per day, one before each meal, one at night before going to sleep, and one before exercising, with an additional difficulty if the physical activity is long.
This control should also be based on the recommendations of the treating physician.
Act quickly in the event of hypoglycemia
When a drop in glucose is common, it is necessary to act quickly and consume about 10 grams of rapidly absorbed carbohydrates or sugar, then wait 10 to 15 minutes and perform a glucose test again.
Generally, when this episode occurs, people need to eat excessively, which undoubtedly helps raise glucose but can generate a rebound effect that can lead to hyperglycemia.
Measure other health indicators
In addition to glucose levels, it is also essential to measure other indicators that help prevent complications closely associated with diabetes, such as cholesterol levels or blood pressure.
This would help to reduce the risk of suffering one of the most frequent complications in diabetic people, such as cardiovascular diseases, especially those affecting blood circulation.
Maintain care of the feet
The lower extremities are one of the most damaged parts when suffering from diabetes. Therefore, they require special attention and care.
The most common symptoms that people with diabetes usually experience in their feet are alterations in sensitivity or a deficit in blood circulation. A daily review is needed to verify that there are no lesions. A doctor should be consulted immediately in case of any distinctive signs.
Regular visits to the ophthalmologist
Another risk that people with diabetes run is to suffer complications related to eye health; therefore, it is recommended to go regularly to an ophthalmologist to check the health of the retina or any other component of sight.
Follow medical treatment to the letter
Last but not least, when suffering from diabetes, one must be very disciplined in complying with the medical treatment prescribed by the treating physician in terms of doses and schedules.
If you experience any side effects, you should immediately notify your doctor so that he or she can evaluate whether there is a need to modify the prescribed medications or their doses.